Maintaining optimal International Normalized Ratio (INR) levels is crucial for individuals on anticoagulant therapy. Patients utilizing PT/INR self-testing monitors must be particularly vigilant, as both dehydration and illness can lead to significant INR fluctuations, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding or thrombotic events.
Understanding INR and Its Importance
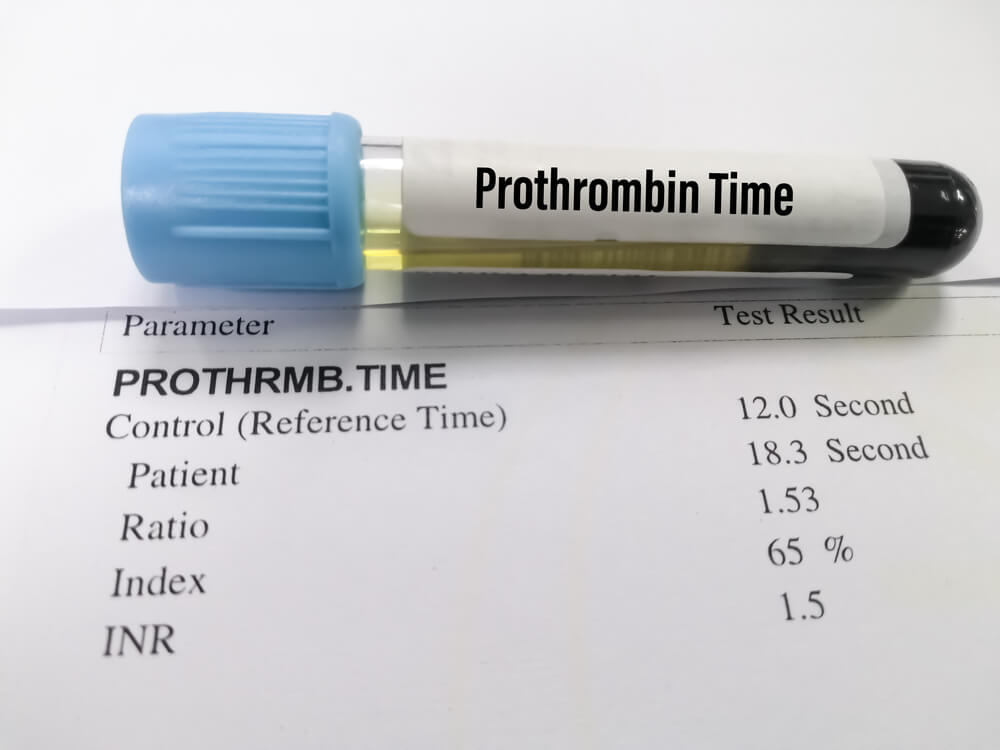
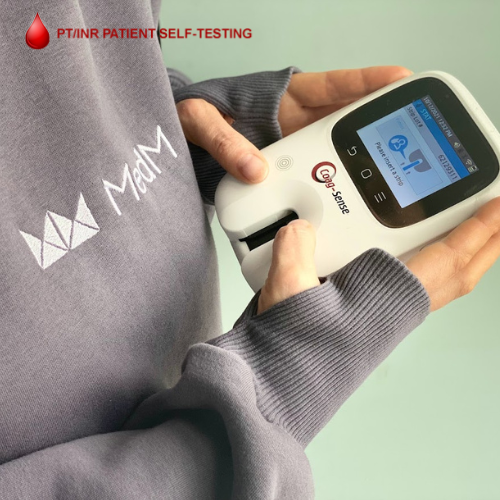
The INR is a standardized measure of how long it takes blood to clot. For patients on anticoagulants like warfarin, maintaining an INR within a target range is vital to prevent complications. Self-monitoring using PT/INR self-testing monitors allows for regular tracking, enabling timely adjustments to therapy
How Dehydration Affects INR Levels
The Physiology Behind Dehydration and Coagulation
Dehydration leads to a reduction in plasma volume, resulting in hemoconcentration. This change can artificially elevate INR readings, as the concentration of clotting factors becomes altered. Additionally, dehydration can impair liver function, where clotting factors are produced, further affecting INR levels.
Clinical Implications
- Elevated INR Readings: Due to hemoconcentration, INR readings may appear higher, increasing the perceived risk of bleeding.
- Risk of Thrombosis: Conversely, dehydration can also lead to a hypercoagulable state, raising the risk of clot formation.
Management Strategies
- Stay Hydrated: Ensure adequate fluid intake, especially during illness or hot weather.
- Monitor Regularly: Use your PT/INR self-testing monitor to track any changes in INR levels during periods of dehydration.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: If significant INR fluctuations are observed, seek medical advice promptly.
Impact of Illness on INR Levels
Mechanisms of Influence
Illnesses, particularly those involving fever, vomiting, or diarrhea, can affect INR levels through various mechanisms:
- Altered Metabolism: Fever can increase metabolic rates, affecting warfarin metabolism.
- Nutritional Changes: Reduced intake or absorption of vitamin K during illness can elevate INR.
- Medication Interactions: Antibiotics and other medications taken during illness may interact with anticoagulants.
Clinical Considerations
- Increased INR Variability: Illness can lead to unpredictable INR levels, necessitating closer monitoring.
- Risk of Complications: Both elevated and reduced INR levels during illness can increase the risk of bleeding or clotting events.
Management Strategies
- Frequent Monitoring: Increase the frequency of INR testing during periods of illness.
- Communicate with Healthcare Providers: Inform your doctor about any illnesses and medications taken.
- Adjust Therapy as Needed
- Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on INR readings and clinical status.
Utilizing PT/INR Self-Testing Monitors Effectively
PT/INR self-testing monitors are valuable tools for managing anticoagulation therapy, especially during periods of dehydration or illness.
Advantages
- Convenience: Allows for frequent monitoring without frequent clinic visits.
- Timely Adjustments: Facilitates prompt therapy modifications based on real-time INR readings.
- Enhanced Engagement: Empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
Best Practices
- Regular Testing: Establish a routine testing schedule and adhere to it.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a log of INR readings, dietary changes, illnesses, and medications.
- Device Maintenance: Ensure the monitor is calibrated and functioning correctly.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Certain signs and symptoms during dehydration or illness warrant immediate medical evaluation:
- Unusual Bleeding: Nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or blood in urine/stool.
- Signs of Clotting: Swelling, pain, or redness in limbs; shortness of breath.
- Significant INR Changes: Sudden spikes or drops in INR readings
Prompt communication with healthcare providers ensures timely interventions and reduces the risk of complications.
YOU MAY GO THROUGH OUR BLOGS TOO:
LIVER DISEASE & BLOOD CLOTTING: WHY INR TESTING IS ESSENTIAL FOR LIVER PATIENTS
EMPOWERING PATIENTS: HOW PT/INR SELF-TESTING ENHANCES ANTICOAGULATION MANAGEMENT
THE ROLE OF PT/INR SELF-TESTING IN IMPROVING PATIENT COMPLIANCE
SUMMARY
Understanding how dehydration and illness impact INR levels is crucial for patients on anticoagulant therapy. By utilizing PT/INR self-testing monitors effectively and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, patients can navigate these challenges safely. Regular monitoring, adequate hydration, and prompt medical consultation during illness are key strategies in managing INR levels and ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Stay proactive in managing your health. Utilize your PT/INR self-testing monitor regularly, maintain hydration, and consult your healthcare provider during any illness. Your vigilance is vital in ensuring the effectiveness and safety of your anticoagulant therapy.